Composting at home is not just an *eco-friendly* practice. It’s also a rewarding way to make *homemade fertilizer* from kitchen scraps and yard waste. By starting *DIY composting*, you help the environment and cut down your organic waste.
For beginners, knowing how to compost is key to better gardening and rich soil. This guide will cover everything you need to learn this important skill.

Introduction to Composting
Composting is key for a green lifestyle. It turns organic matter into nutrient-packed soil. By composting at home, you cut down on landfill waste and help recycle organic matter.
Composting is good for our planet and makes soil healthier. It uses kitchen leftovers, yard waste, and more to feed plants. This process teaches us about reducing waste and supports eco-friendly actions.
What is Composting?
Composting turns organic matter into nutrient-rich soil called compost. It uses microorganisms, worms, and decomposers to break down food scraps and yard waste. It’s a key part of organic waste recycling. This process helps us reduce waste and improve our gardens.
There are many composting techniques for different needs. Two popular ones include:
- Hot composting keeps the compost pile warm to speed up decomposition and kill germs.
- Cold composting is slower, letting materials break down naturally over time. It’s great for beginners.
The composting process needs a mix of green and brown materials. Greens like vegetable scraps provide nutrients. Browns like dried leaves help with airflow. This mix is vital for the decomposers’ work.
Learning the basics of composting lets you help reduce landfill waste. It also gives you great compost for your garden. Embracing composting boosts sustainability and soil health. It makes your backyard ecosystem thrive.
Benefits of Composting at Home
Composting at home has many advantages. It helps us live more sustainably. Turning kitchen scraps and yard waste into nutrient-rich material cuts down on landfill waste. It eases environmental pressure and boosts soil health by adding back valuable organic matter.
Making your own fertilizer is a key benefit of composting. This natural fertilizer improves soil, holds more water, and feeds plants essential nutrients. It results in healthier gardens and less need for harmful chemical fertilizers.
Composting also saves water. Soil with compost holds water better, reducing how often you need to water your garden. This makes gardening more sustainable, helping the environment and lowering carbon emissions.
People who compost see real benefits. They have lower trash bills, healthier gardens, and strong community ties. As more people learn about composting, they join in. This movement leads to a hopeful, sustainable future.
Choosing the Right Composting Method
Picking the right composting method is crucial for beginners wanting to compost at home. Every composting system has its own benefits. It’s key to think about your space, budget, and what you prefer.
There are a few composting methods perfect for those just starting out:
- Traditional Compost Bins: These bins offer a confined area for organic waste. Keeping an eye on moisture and air flow helps compost faster.
- Tumblers: Tumblers make turning compost easy, promoting quick decay. They’re great for small areas.
- Vermicomposting: This method uses worms to break down waste. It’s super for tight spaces and creates rich compost.
Deciding on a composting method depends on your specific needs:
| Composting Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Compost Bin | Cost-effective, large capacity | Takes longer to decompose |
| Tumbler | Quick composting, user-friendly | More expensive initially, smaller capacity |
| Vermicomposting | Ideal for indoors, produces top-notch compost | Needs careful upkeep, worm costs |
After reviewing these options with your personal scenario in mind, you’ll pinpoint the ideal method for your composting adventure. Adopting DIY composting practices benefits your garden and supports a greener planet.
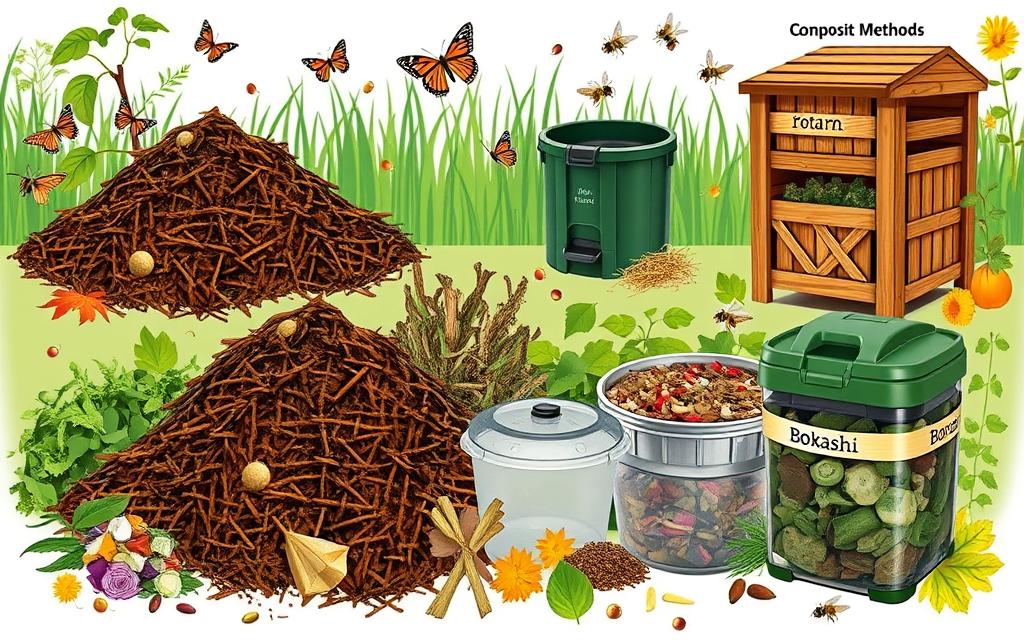

What Can You Compost?
Backyard composting is a great way to turn organic waste into rich soil. It’s important to know what things can be composted. We usually divide compostable stuff into ‘green’ and ‘brown’ categories.
Green materials are packed with nitrogen. They include:
- Vegetable scraps
- Fruit peels
- Coffee grounds
- Grass clippings
- Plant trimmings
Brown materials, on the flip side, are loaded with carbon. Examples are:
- Dry leaves
- Straw
- Pine needles
- Cardboard
- Paper (shredded)
To make great compost, mix three parts brown with one part green. This balance speeds up decomposition. It also creates top-notch compost.
Knowing what not to compost is also key. Do not add:
- Dairy products
- Meat and bones
- Oils and fats
- Diseased plant material
- Pests or chemical-treated items
Choosing the right materials for your compost pile helps the environment. It makes soil healthier and supports green gardening.
Setting Up Your Composting Bin
Setting up a good composting bin is key for quality backyard composting. First, pick a good spot. It should be easy to get to but also in the shade to keep it moist. A really dry or sunny spot can slow down the breaking down process.
Then, choose if you want to make your bin or buy one. If you like to build things, using wooden pallets or wire mesh might be fun. But, you can also find bins ready to buy at stores for gardening. Think about how much stuff you will compost and the space you have in your yard.
After you’ve picked a spot and bin, getting your compost mix right is next. You need both nitrogen-rich greens, like kitchen leftovers and grass, and carbon-rich browns, like dry leaves and cardboard. The best mix is about three parts brown for every one part green. This helps everything break down well.
Stir your compost pile often to let air in and help it decompose faster. Keep it moist, but don’t make it too wet. This keeps the microorganisms happy so your compost bin works great. By following these tips, your composting will be successful and eco-friendly.
The Composting Process
The composting process includes key stages for breaking down organic material. It’s crucial to understand these steps for successful home composting. The breakdown depends on moisture, air, and heat.
To get the right conditions, focus on the following:
- Moisture: The correct moisture level is critical. Too much water causes a lack of air, while too little slows decomposition.
- Aeration: Good air flow keeps the compost healthy. Mix the pile often to let in oxygen needed by microbes.
- Temperature: Heat is produced by microbes breaking down materials. Keep an eye on temperature to ensure things are decomposing well.
There are different ways to compost:
- Bin Composting: Enclosed bins offer a controlled environment for breaking down waste.
- Pile Composting: This simple approach uses a loose pile of materials. Turn it sometimes for better air flow.
- Vermicomposting: Worms help quickly turn waste into high-quality compost.
Watch your compost’s development closely. Check for changes in temperature and how it smells. A healthy pile smells nice and earthy. Bad smells suggest too much moisture or not enough air.
Using Your Finished Compost
Finished compost is excellent for plants and garden beds. It adds rich nutrients and helps soil structure. It also supports microorganisms that are good for plant growth.
Adding compost to your garden is easy. As a garden soil amendment, it boosts nutrient levels and helps soil hold moisture. Just mix it into the soil before planting. Or spread it around plants that are already growing. This lets the nutrients slowly reach the soil, helping plants over time.
Using compost as a top dressing can make your plants healthier. A 1 to 2 inch layer on your garden beds can fight weeds and feed your plants. Homemade fertilizer from compost also attracts helpful bugs, helping the whole ecosystem.
For pots, finished compost is a great ingredient in potting mix. Combine it with peat moss or perlite. This mix holds moisture well and feeds plants effectively.
Make sure your compost is fully mature before you use it. Fully matured compost breaks down materials well. This makes it more effective and beneficial. With the right use, compost can make your garden flourish.
| Application Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Amendment | Mixing compost into existing garden soil before planting. | Improves nutrient availability and soil texture. |
| Top Dressing | Applying a thin layer of compost on the soil surface. | Suppresses weeds and gradually nourishes plants. |
| Container Mix | Combining compost with other materials for potting soil. | Enhances moisture retention and nutrient supply. |
Conclusion
Composting is more than just a simple activity; it’s key for sustainable living. With easy tips, you can turn kitchen scraps and yard waste into valuable compost. This helps your garden and the Earth.
Composting does more than improve soil; it cuts down landfill waste and encourages eco-friendly living. Starting is easy. Just take it step by step, adding more as you get used to it. This green habit helps the planet and makes gardening better.
Getting into composting means making a big difference with small steps. With each bit of compost, we show how we all can help our world. Ready for more on composting? There’s plenty of info out there with tips and tricks. Start your sustainable living journey at home and inspire others!
FAQ
What are the basic steps for composting at home?
To start, pick a spot for your compost bin or pile. Gather both ‘green’ (rich in nitrogen) and ‘brown’ (rich in carbon) materials. Keep it moist and aerate it often.
Watch your compost by checking its warmth and how well it breaks down.
What materials should I avoid putting in my compost?
Don’t compost dairy, meat, oils, or cooked foods, as they may attract pests and smell bad. Also, avoid adding pet waste and sick plants to your compost.
How long does it take for compost to break down?
The composting time varies, taking weeks to months. Factors like warmth, wetness, air, and the materials impact this. Hot composting is quicker than cold composting.
Can I compost in an apartment without a backyard?
Yes! Try worm bins (vermicomposting) or bokashi composting for small spaces. They’re great for breaking down kitchen waste without needing much space.
How do I use my finished compost in the garden?
Use mature compost to enrich garden soil, as a top layer for plants, or mix into potting soil. It boosts fertility in the garden.
What are the environmental benefits of composting?
Composting cuts down organic waste in landfills and reduces greenhouse gases. It enriches soil, supports garden diversity, and fosters sustainable nutrient cycles. All this aids eco-friendly gardening.
How can I maintain a healthy compost pile?
For a healthy pile, turn the mix for air, keep it damp (not wet), and balance greens and browns. Checking its temperature and for bad smells helps ensure effective composting.