Did you know permaculture was started by David Holmgren and Bill Mollison? It’s a new way to live sustainably. It focuses on taking care of the Earth and building strong communities. With our planet facing big environmental problems, we need sustainable living more than ever.
Permaculture is based on three main ideas: Earth care, People care, and Future care. These ideas help us connect with nature and use resources wisely. It aims to create systems that are not just sustainable but also grow stronger over time. This way, communities can better face climate change and live in harmony with their environment.
In this article, you’ll learn how permaculture can turn your community into a strong, green haven. It’s a way to prepare for the future and improve health for all.
Understanding Resilient Communities
Resilient communities can face and bounce back from tough times, like natural disasters and economic hard times. They help people do well, even when things get hard. This makes them strong and supportive.
What is a Resilient Community?
A resilient community gets ready for disasters and builds strong bonds among its people. They focus on disaster preparedness to lessen the blow of crises. It’s about working together and helping each other out when needed.
Key Characteristics of Resilient Communities
Several things make resilient communities strong. Key traits include:
- Strong social networks: People who support each other can tackle challenges better.
- Accessible resources: Having health and social services helps in recovering from disasters.
- Sustainable infrastructure: Good infrastructure can stand up to environmental challenges.
- Active disaster preparedness: Regular planning and training prepare communities for emergencies.
- Effective public health systems: A strong health system is key to keeping people healthy and preventing disease.
With 85% of the world noticing climate change, building resilience is more crucial than ever. Black and African American communities face higher risks, like more heat-related health issues. It’s vital to address these injustices to build resilience.
To build resilience, we need more government help in planning and talking to the community. Supporting programs for at-risk groups strengthens community bonds. After disasters, people often come together more, making communities closer.
| Characteristic | Importance |
|---|---|
| Strong Social Networks | Enhances support and collaboration during crises |
| Accessible Resources | Facilitates quick recovery and well-being |
| Sustainable Infrastructure | Reduces vulnerabilities to environmental stresses |
| Active Disaster Preparedness | Equips communities to handle emergencies efficiently |
| Effective Public Health Systems | Supports population health and reduces disease spread |
The Principles of Permaculture
Permaculture is a way to design that connects all living things. It helps us create sustainable projects that work with nature. The core of permaculture is its ethics, which guide us in building strong ecosystems and communities.
Ethics and Design Principles
The main ethics of permaculture are:
- Care for the Earth: Keeping our planet healthy for the future.
- Care for People: Helping communities and individuals succeed.
- Fair Share: Sharing extra resources for everyone’s benefit.
These ethics shape many permaculture principles, like:
- Observe and interact
- Catch and store energy
- Obtain a yield
- Apply self-regulation and feedback
- Use and value renewables
- Produce no waste
- Design from patterns to details
- Integrate, don’t segregate
- Use small, slow solutions
- Use and value diversity
- Use edges and value the marginal
- Creatively use and respond to change
By using these principles, we can build systems that support sustainable growth and ecological balance.
Zones and Sectors in Permaculture
Knowing about zones and sectors is key to good permaculture design. Zones are different areas based on how much care they need. For example:
| Zone | Description | Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Zone 1 | High-maintenance areas, like vegetable gardens. | Daily care and harvesting. |
| Zone 2 | Moderate-maintenance areas, such as herb gardens. | Weekly maintenance. |
| Zone 3 | Low maintenance, including orchards. | Seasonal harvesting. |
| Zone 4 | Managed forests or wild areas. | Occasional visits for resources. |
| Zone 5 | Wilderness areas for biodiversity. | No intervention. |
By organizing zones well, we can be more efficient and use fewer resources. This approach helps us create a caring environment for both people and the planet.
Benefits of Permaculture for Your Community
Permaculture in your community offers many benefits. It helps the environment, boosts the economy, and brings people together. By using permaculture, you help create a better world for everyone.
Environmental Impact
Permaculture has a big positive effect on the environment. It increases biodiversity and improves soil health. It also saves water and doesn’t use harmful chemicals.
By using natural systems, permaculture creates self-sustaining ecosystems. This means less pollution and healthier food. Plus, it helps cities reduce their carbon footprint by adding green spaces.
Economic Advantages
Permaculture can also save money. It reduces the need for industrial farming, which is bad for the environment. By growing your own food, you support a sustainable economy.
Communities that use permaculture often see more jobs and economic growth. For example, the Beacon Food Forest in Seattle shows how to turn urban land into productive farms. This lowers costs for people living nearby.
Social Cohesion
Permaculture helps communities come together. Gardening and learning together builds strong relationships. It creates a supportive network of people.
As permaculture groups grow, they offer chances to work together and share resources. This improves overall happiness and a sense of belonging. The Sherrett Food Forest in Portland is a great example of how community gardens can unite neighborhoods.
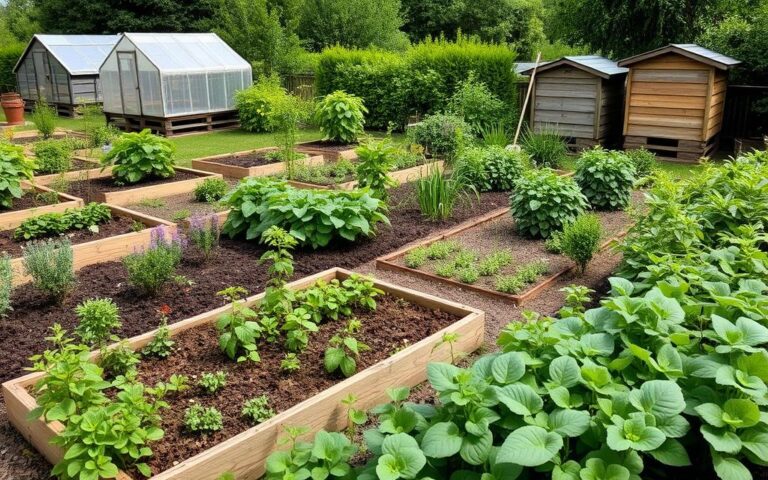
Creating a Permaculture Garden
Starting a permaculture garden is a rewarding way to connect with nature and help the planet. It involves several steps to make your garden a thriving ecosystem. Here are some tips to help you get started.
Steps to Start Your Garden
To start your permaculture garden, first assess your site. Note the sunlight, water, and plants already there. This info will guide your design.
- Check your local climate and soil.
- Map out zones for sun and plant needs.
- Design a layout for biodiversity and self-sustaining growth.
Choosing the Right Plants
Choosing the right plants is key to your garden’s success. Pick a variety that works well together. Focus on:
- Native and drought-resistant plants to save water.
- Perennial veggies and fruit trees for ongoing harvests.
- Cover crops to boost soil health and prevent erosion.
Maintenance Tips for Long-term Success
After your garden grows, regular care keeps it thriving. Follow these tips for ongoing success:
- Use mulch to keep moisture in and weeds out.
- Practice companion planting to boost growth and fight pests.
- Compost regularly to enrich your soil.
Creating a permaculture garden does more than help the environment. It also builds community. By following these steps, your garden will flourish, supporting biodiversity and resilience for years to come.
Educating Your Community on Permaculture
Teaching your community about permaculture is key to living sustainably. Workshops and hands-on learning help a lot. They make people understand and use ecological ideas.
Workshops and Learning Opportunities
Workshops are great for teaching about permaculture. They include:
- Hands-on gardening demonstrations
- Discussions on ecological design principles
- Training on community outreach strategies
- Fundraising techniques for local projects
These activities help people work together. They also teach how to use permaculture in everyday life. This makes the community stronger.
Creating a Community Garden
A community garden is a great place to learn. It has many benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | Encourages teamwork among community members. |
| Food Security | Enhances access to fresh produce within the neighborhood. |
| Environmental Connection | Strengthens the relationship between individuals and nature. |
| Social Interaction | Facilitates gatherings and fosters friendships. |
Creating a community garden enriches community life. It lets everyone learn and share in sustainable practices.
Resilient Communities and Climate Change
Climate change is a big problem, and we need strong communities to fight it. Permaculture is a key tool in this fight. It makes local ecosystems better and helps communities deal with environmental changes.
How Permaculture Helps Combat Climate Change
Permaculture creates systems that improve soil and bring back biodiversity. This helps lower harmful emissions and ensures food is grown locally. It also cuts down on the need for fossil fuels.
Using solar power is another way to reduce carbon emissions. This makes communities more sustainable.
Adapting to Local Climate Conditions
Understanding local weather is key to fighting climate change. Planting native plants makes gardens strong against bad weather. Teaching people about caring for the environment helps them adapt better.
Using rainwater and making green spaces can also help. When communities share knowledge, they can tackle climate issues more effectively.
| Strategy | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Companion Planting | Planting different crops together to benefit each other | Increases biodiversity and reduces pests |
| Rain Gardens | Landscaped areas that collect and absorb rainwater | Helps manage stormwater and recharge local aquifers |
| Community Education | Workshops on sustainable practices | Empowers residents to take action against climate change |
| Urban Green Spaces | Creation of parks and green roofs in urban areas | Enhances air quality and provides cooling effects |
Case Studies: Successful Resilient Communities
In the United States, many communities have shown how to be resilient. They have used permaculture and green infrastructure. These examples are great for learning how to make your community more sustainable and resilient.
Examples Across the United States
Many cities have started projects to solve environmental problems. For example:
- Philadelphia is looking at both old and new ways to handle water overflow.
- The Great Lakes Restoration Initiative has helped sixteen cities along the Great Lakes. They got grants to fix their ecosystems.
- In Asheville, North Carolina, the city used a special tool to plan for the future. They wanted to be ready for any challenges.
- Florida’s strawberry farmers use a digital tool. It helps them manage diseases and save money.
Lessons Learned from Their Experiences
These successful stories teach us a lot:
- Getting local people involved makes projects better and more effective.
- Using green solutions helps the environment now and saves money later.
- Working together with local governments and groups helps solve big problems.
- Adopting new green technologies helps meet today’s needs and tomorrow’s challenges.
These lessons can help your community become more resilient. By learning from others, you can find the best way to make your community strong. This will help you face challenges and inspire others to do the same.
| City | Key Initiative | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Philadelphia | Combined Sewer Overflow Management | Improved water quality |
| Asheville | Climate Resilience Planning | Proactive hazard management |
| Great Lakes Region | Restoration Grants | Enhanced ecosystem health |
| Menominee Nation | Climate-informed Reforestation | Faster forest regeneration |
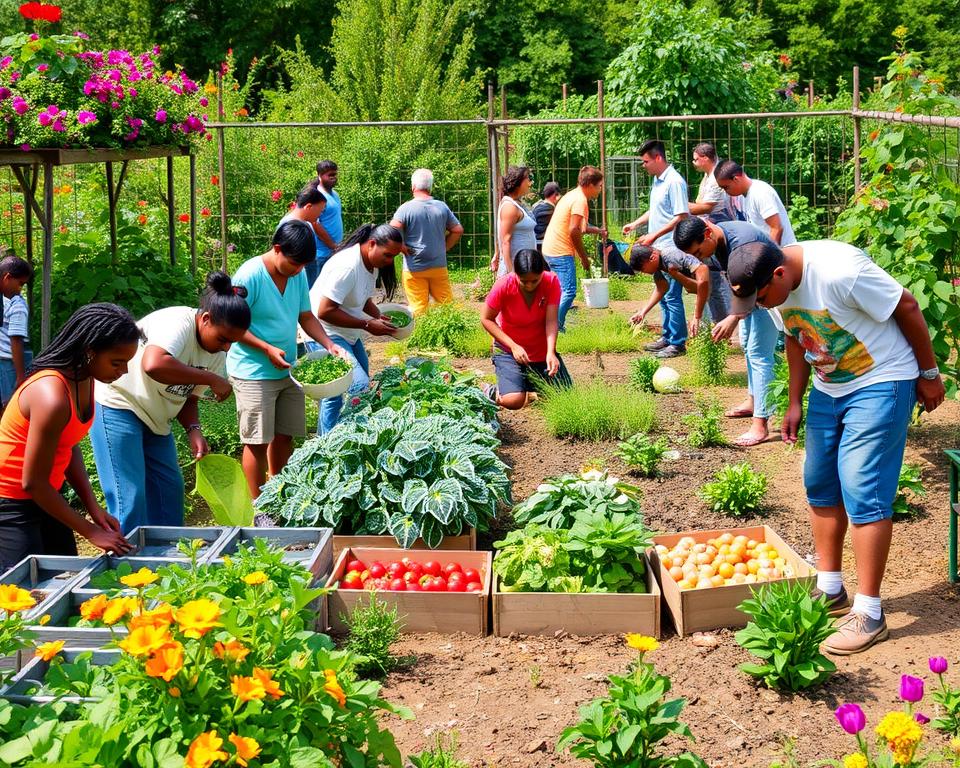
Engaging with Local Organizations
Working with local groups makes permaculture projects better and builds strong communities. By teaming up with environmental groups and local farmers, communities get more support for their green efforts.
Partnering with Environmental Groups
Team up with environmental groups to share knowledge and resources. These partnerships can bring:
- Access to funding for projects that help the planet.
- Training programs to teach volunteers about saving the environment.
- Networking chances to meet others who care about the planet.
Building Networks with Local Farmers
Connecting with local farmers is key for a healthy permaculture community. This helps with:
- Resource sharing, so farms can work together and share tools.
- Experiential learning through workshops and farm tours to teach about green living.
- Market access for people to buy fresh, local food, helping the local economy.

| Engagement Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Environmental Partnerships |
|
| Local Farmers Networks |
|
Putting a lot of effort into working with local groups is important. It builds strong networks and strengthens the community. Together, communities can reach their green goals and become more resilient against challenges.
The Future of Resilient Communities and Permaculture
The future of strong communities is linked to permaculture. This is because more people are moving towards living sustainably. Urban permaculture is becoming popular, focusing on local food and community support.
Cooperative groups are now choosing sustainable paths. This shows a big push for taking care of the environment and fairness. It matches the United Nations’ goals for a better world.
Trends in Sustainable Living
People are finding ways to use permaculture in their everyday lives. It’s all about using resources wisely and valuing what can be renewed. By starting small, we can learn and grow together, building a sustainable culture.
Permaculture farms show us how to improve soil and increase food variety. They also help us face climate challenges better.
How You Can Get Involved
You can help make a difference by joining local groups or learning at workshops. Starting projects like urban gardens or farmers’ markets grows food and brings people together. By working together, we can make a big change.
We can focus on using renewable energy and reducing waste. This way, we ensure a better future for all of us.