Did you know homes with passive solar design can save up to 50% on energy bills? This is compared to houses built the traditional way. It shows how powerful Passive Solar Design is in making homes both energy-efficient and sustainable.
This method uses the sun’s energy to cut down on the need for heating and cooling. It brings economic and environmental gains to homeowners.
By carefully choosing the home’s orientation and where to place windows, you can make it more energy-efficient. This design also uses thermal mass to keep your home comfortable. In this article, we’ll dive into the key parts of Passive Solar Design.
We’ll share tips to help you make your home more eco-friendly. This will improve your living space and support sustainable building practices.
Understanding Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design uses the sun’s energy for heating and cooling. It combines natural elements with architecture for better comfort and less energy use. This approach makes buildings look good and supports green building goals.
What Is Passive Solar Design?
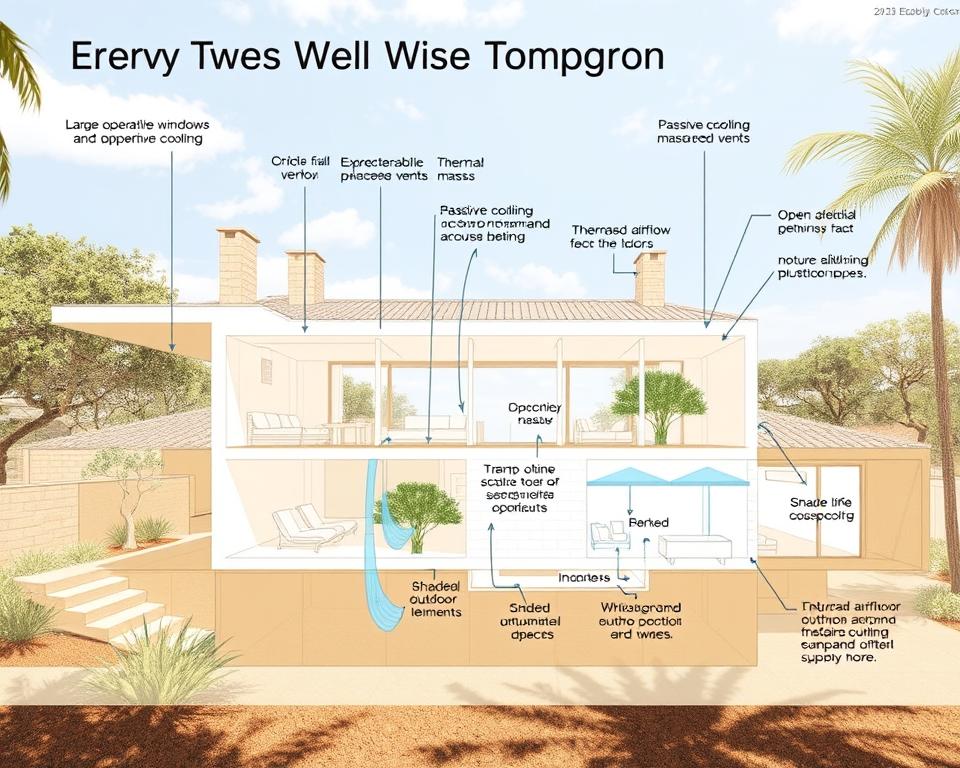
Passive solar design uses the sun to control a building’s temperature without machines. Architects place windows right to catch sunlight in winter. In summer, they use design to keep it cool and breezy.
This natural method saves money by needing less artificial systems.
Key Principles of Passive Solar Design
Good passive solar design follows a few key rules:
- Orientation: Most windows should face south to get more sunlight.
- Thermal Mass: Use materials like concrete to soak up and keep heat from sunlight.
- Shading: Use overhangs or plants to block too much summer sun but let winter sun in.
Knowing these helps make buildings more energy-efficient and comfortable, saving money too.
Benefits of Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design offers many benefits:
- Lower Energy Bills: Using less energy means big savings on bills.
- Increased Comfort: Stable temperatures make homes more comfortable.
- Environmental Impact: Using less energy means less pollution, helping the planet.
These benefits show why using passive solar design is important for green buildings.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Significant reduction in energy expenses due to enhanced efficiency. |
| Comfort | Stable internal temperatures lead to improved living conditions. |
| Reduced Carbon Footprint | Lower emissions support a healthier environment, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. |
How Orientation Affects Energy Efficiency
Your home’s direction is key to saving energy. The right solar orientation lets in more natural light. This follows the principles of passive solar design.
A home facing south gets warm sunlight in winter, cutting heating costs. Positioning your home 30 degrees from true south optimizes sunlight. This also helps avoid overheating in summer.
Ideal Orientation for Homes
For homes to be energy-efficient, the right direction is crucial. Here are some important points:
- South-facing homes get more sunlight, which lowers heating costs.
- Buildings longer than wide should face east-west for best solar heat.
- Place windows and skylights to catch natural light without glare.
The Role of Windows and Sunlight
Daylighting strategies are key for window placement and size. Big windows and skylights let in sunlight, cutting down on artificial light. This natural light saves energy, boosts mood, and increases productivity.
When picking windows, look for low-emissivity coatings and gas fillings. These features help keep the right balance of heat and sunlight.
Seasonal Sun Path Considerations
Knowing the sun’s path by season is crucial for home design. The sun’s angle changes with the seasons, affecting your home’s orientation. Tools like wind rose diagrams help align your home with winds for natural ventilation.
This design choice improves comfort without using too much energy. By focusing on natural resources, your home becomes more sustainable.
| Orientation | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| South-Facing | Maximized sunlight for heating | Minimize windows on the north side for better insulation |
| East-West | Balanced daylight throughout the day | Pay attention to shading from trees and buildings |
| North-Facing | Less solar heating in warmer months | Consider increased insulation on this side |
Choosing the Right Windows
Choosing the right windows is key for a good passive solar design. Energy-efficient windows help lower your energy bills by using natural sunlight and keeping energy in. Knowing about different window types and where to put them can make your home more comfortable and green.
Types of Energy-Efficient Windows
There are many energy-efficient windows out there, each aimed at saving energy:
- Double-glazed windows: These have two panes of glass with a gap in between, cutting down on heat loss.
- Low-emissivity (Low-E) glass: This glass has a special coating that keeps heat in while letting sunlight in.
- Gas-filled windows: Filled with gases like argon or krypton, these windows are better insulators than air-filled ones.
- High-performance frames: Made from materials like vinyl or fiberglass, these frames are better at keeping heat in than wood or aluminum.
Window Placement for Maximum Gain
Where you put your windows is very important for keeping your home warm and sunny. Here’s how to do it right:
- Put south-facing windows where they get the most sunlight, covering 7% to 15% of your floor.
- Use overhangs to keep your home cool in summer and warm in winter.
- North-facing windows are great for natural light, and Low-E glass helps keep them warm without letting in too much heat.
Glazing Options Explained
Different glazing options can make a big difference in your windows’ performance. Pick the right one based on your climate and energy goals:
| Glazing Type | Benefits | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Single Low-E | Good thermal insulation | Moderate climates |
| Double Low-E | Superior insulation and UV protection | Cold climates |
| Triple Glazing | Excellent energy savings | Very cold climates |

Insulation and Thermal Mass
In the world of energy-efficient homes, insulation and thermal mass are key. Insulation helps keep your home warm or cool, saving energy. It’s important for comfort all year.
Importance of Proper Insulation
Good insulation keeps your home’s temperature steady. It’s best to put insulation outside, near thermal mass. This way, your home can hold onto warmth in winter.
Without enough insulation, your home can’t keep warm or cool well. This means you’ll use more energy and pay more for it.
Materials That Enhance Thermal Mass
Choosing the right materials boosts insulation and thermal mass. Some top picks are:
- Concrete
- Brick
- Adobe plaster
- Tiles
- Rock (sandstone)
Using Structure Insulated Panels (SIPs) or Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs) is smart. They mix insulation and thermal mass well. Knowing about these materials helps you make your home more energy-efficient.
How Thermal Mass Works in Your Home
Thermal mass absorbs, stores, and releases heat slowly. In the day, materials like concrete or stone soak up the sun’s heat. At night, they give off that heat, keeping your home cozy.
In summer, thermal mass helps keep your home cool. It absorbs extra heat, making your space comfortable.
Knowing about sun angles is key for using thermal mass right. Placing materials wisely can make your home more energy-efficient. This works in many climates, making your home more comfortable.
Landscaping for Passive Solar Design
Landscaping is key to making passive solar design work better. By planning your outdoor space well, you can help your home use energy more efficiently. This not only makes your home more comfortable but also helps the environment.
Strategic Planting for Shade and Light
Planting shade trees in the right spots can cool your home in summer and let sunlight in winter. Choose deciduous trees that fit your local climate. They offer shade in summer and let sunlight through in winter, helping your home get the right amount of sun.
The south side of your house gets the most sunlight. This is a great spot for trees that provide shade and let sunlight through.
Native Plants That Benefit the Environment
Using native plants in your landscaping can save you money and water. These plants are made for your local climate, so they need less care. They also help your local ecosystem by attracting good wildlife and keeping your home looking natural.
The Role of Hardscaping in Efficiency
Things like pathways, patios, and walls are important for passive solar design. They help keep your home warm in winter and cool in summer. By choosing materials that absorb or reflect heat well, you can make your outdoor space more comfortable.
| Element | Function | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Deciduous Trees | Provide shade in summer, sun in winter | Energy conservation, reduced cooling costs |
| Native Plants | Require less maintenance and water | Support local ecosystem, cost-effective |
| Hardscaping Features | Influence thermal dynamics | Enhanced energy efficiency, aesthetic appeal |
Ventilation Strategies
Keeping your home cool is key. In a passive solar home, using natural ventilation is a smart move. It helps cool your space without needing air conditioning.
Just open your windows to let in the breeze. This simple step can make your home feel cooler and more comfortable.
Natural Ventilation Techniques
Natural ventilation brings fresh air into your home. Here are some ways to do it:
- Open windows to catch the breeze.
- Use night ventilation to cool your home when it’s hot outside.
- Operable skylights add more airflow.
These methods help cool your home naturally. They use the climate to your advantage.
Using Cross Ventilation to Your Advantage
Cross ventilation improves air flow by creating a path through your home. Place windows on opposite sides to let cool air in and warm air out. This keeps your home comfortable.
It’s important to match your windows with the wind direction. Think about your neighborhood and how your home is built.
Benefits of Stack Ventilation
Stack ventilation uses heat to move air. Warm air goes up and out, while cool air comes in. This method helps cool your home naturally.
Using these strategies can save you money on energy. They keep your home cool and comfortable without relying on air conditioning.
| Ventilation Strategy | Benefits | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Ventilation | Reduces reliance on mechanical systems. | Ensure effective window placement. |
| Cross Ventilation | Maximizes cooling efficiency. | Align with prevailing wind directions. |
| Stack Ventilation | Promotes air circulation using thermal dynamics. | Implement higher openings for warm air exit. |
Incorporating Renewable Energy
Adding renewable energy systems to your home boosts efficiency and sustainability. Solar panels, for example, work well with passive solar design. They help capture energy all year, cutting down on traditional energy use and bills.
How Solar Panels Complement Passive Design
Solar panels are key in enhancing passive solar designs. They turn sunlight into power or hot water, meeting your heating and energy needs. This mix of passive and solar techniques creates a balanced, efficient system.
Exploring Other Renewable Options
Look into other renewable sources for better energy efficiency. Wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass are great alternatives. Each offers unique benefits, fitting well with passive design.
Integrating Passive and Active Systems
Combining passive and active systems makes your home sustainable and resilient. Using natural elements like sun, wind, and water keeps your home comfortable without needing mechanical systems. Tools like RETScreen, HOMER, and PHPP help plan these systems for your home.
| Renewable Energy Source | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Energy | Reduces energy costs, lowers emissions | Initial cost, space requirements |
| Wind Energy | Clean electricity generation | Variability, noise |
| Geothermal Energy | Consistent temperature regulation | Installation complexity |
| Hydro Energy | Reliable power source | Environmental impact, location-dependent |
| Biomass | Reduces waste, renewable resource | Management and transportation costs |
Passive solar design can lead to LEED certification and empower consumers. Exploring renewable energy options keeps your home efficient and eco-friendly.
Cost Considerations and Savings
Understanding the costs of passive solar design is key for homeowners. The initial cost can be higher than traditional methods. Yet, the long-term savings make it worth considering.
Adding energy-efficient features can cut down on energy bills. This makes passive design appealing for those wanting a more efficient home.
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
At first, the cost might seem high. But, passive solar design can save up to 80% on heating and cooling. This helps balance the initial investment.
Investing in quality windows, insulation, and shading can lower costs over time. It’s a smart move for long-term savings.
Government Incentives for Passive Design
Government incentives can ease the financial burden of passive solar design. These include tax credits, rebates, and grants for energy efficiency. Homeowners should look into these to save more.
Evaluating Payback Periods
Understanding payback periods is crucial. It shows when savings from energy efficiency equal the initial cost. A well-designed passive solar home often offers quick payback times.
| Expense Type | Estimated Initial Cost | Annual Savings | Payback Period (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Performance Windows | $10,000 | $1,500 | 6.7 |
| Insulation Enhancements | $8,000 | $1,200 | 6.7 |
| Solar Orientation Improvements | $5,000 | $700 | 7.1 |
| Shading Devices and Overhangs | $7,000 | $1,000 | 7.0 |
By looking at these costs and savings, you can make smart choices. These choices benefit your wallet and the environment.
Real-World Examples of Passive Solar Homes
Looking at real-world examples of passive solar homes shows their success. These homes use southern exposure, thermal mass, and natural ventilation. They save up to 80% of energy compared to regular buildings.
With over 39,000 certified passive houses in the U.S., it’s clear they work well. These designs offer real benefits.
Case Studies of Successful Designs
The Foyle House is a great example. It follows Passive House standards and won House of the Year Ireland 2019. In Ladakh, Wangchuk’s houses use local materials and modern tech for sustainability.
These homes might cost more upfront, but save a lot of energy in the long run. They show that sustainable homes are not just dreams but real possibilities.
Lessons Learned from Innovative Projects
These examples teach us a lot about sustainable building. Wangchuk’s work shows the power of community in sharing knowledge. Architects are working hard to reduce emissions and meet the demand for green homes.
Learning from these projects helps you make better choices. You can design homes that are both efficient and good for the environment.