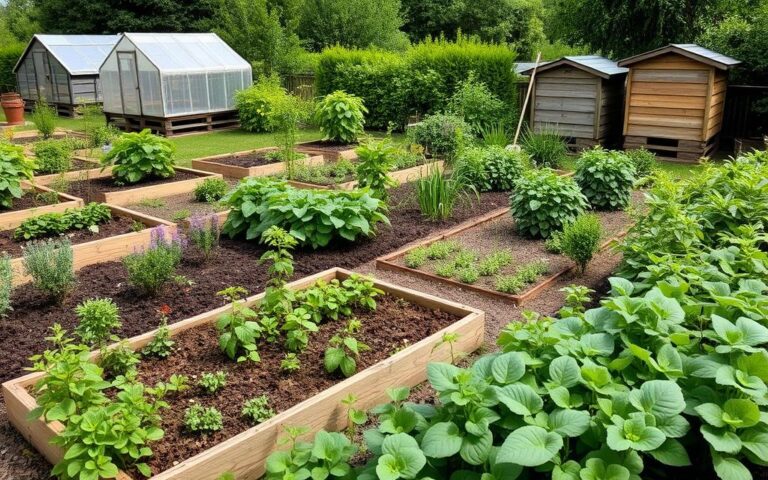
Did you know over 40% of the world’s food is grown organically? Yet, only about 1% of farmland is used for organic farming? This shows how much potential there is for sustainable practices like permaculture in gardening. By using ecological systems, you can make a garden that feeds you and helps nature.
This guide will teach you about permaculture and how it boosts organic gardening. You’ll learn how these practices improve soil, save water, and use plants that fit your area’s climate. A permaculture garden is more than just growing food. It’s a living system that works with nature.
Understanding Ecological Systems in Your Garden
Starting a sustainable organic garden means understanding the complex relationships in ecological systems. This knowledge helps you create a garden that supports biodiversity, improves soil health, and aids in sustainability.
What Are Ecological Systems?
Ecological systems are made up of living things and their environment, working together. They can be small gardens or big landscapes, each balancing living and non-living parts. In your garden, focusing on these systems lets you see how everything connects, helping plants grow and supporting many species.
The Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is key to a healthy ecosystem. A variety of plants, insects, and microorganisms makes your garden strong against pests and diseases. Growing different species, like native plants, helps local wildlife and keeps the ecosystem balanced. This diversity makes your gardening more sustainable.
How Soil Health Affects Plants
Soil health is crucial for a garden’s success. Healthy soil is full of nutrients and tiny life forms that plants need to grow. By composting, mulching, and using cover crops, you can make your soil better. This helps your plants grow well, making your garden a sustainable haven.
The Basics of Permaculture Principles
This section explores the core ideas of permaculture. It shows how these ideas help us garden in a sustainable way. Permaculture mixes ecological design with ethics, creating a strong base for managing natural resources.
The Seven Principles of Permaculture
The seven principles of permaculture guide us in making sustainable ecosystems. They include:
- Observe and Interact: It’s important to understand your surroundings before making changes.
- Catch and Store Energy: Using resources efficiently makes our systems more sustainable.
- Obtain a Yield: Make sure your system gives back to you and the environment.
- Apply Self-Regulation and Accept Feedback: Adjusting based on results helps improve your practices.
- Use and Value Renewable Resources: Focus on sustainable practices that keep our resources intact.
- Design from Patterns to Details: Use nature’s patterns in your designs.
- Integrate Rather Than Segregate: Connect elements to boost system efficiency.
How Permaculture Mimics Nature
Permaculture design takes cues from nature. It uses successful patterns found in ecosystems. This leads to:
- Synergistic Relationships: Elements work together, making systems more resilient.
- Resource Efficiency: Using resources wisely reduces waste and promotes sustainability.
- Long-Term Viability: Creating self-sustaining systems supports continuous growth.
By using permaculture principles, you can create an environment that thrives. It not only survives but also benefits the larger ecosystem. This approach respects and learns from nature, aiming for a sustainable future.
Choosing the Right Location for Your Garden
Finding the ideal location for your garden is key. It should get enough sunlight and have good water management. Also, it should be easy to get to.
Think about how much sunlight your garden needs. Some plants love full sun, while others prefer shade. Make sure your garden gets the right amount of sunlight.
Water management is also important. Your garden should have good drainage to avoid waterlogged soil. Make sure the soil drains well and use proper irrigation systems.
Accessibility is another thing to consider. Your garden should be easy to get to. This makes it easier to tend to your plants and enjoy your garden.
By choosing the right location, you can create a beautiful and functional garden. It will be a place where you can relax and enjoy nature.
Benefits of Choosing the Right Location for Your Garden:
- Optimal sunlight for plant growth
- Effective water management to prevent waterlogged soil
- Easy accessibility for maintenance and enjoyment
Designing Your Permaculture Garden Layout
Creating a good garden layout is key to making your garden productive and balanced. This section will cover two main strategies: companion planting and permaculture zones. These methods help improve your garden design by using space well and enhancing plant relationships.
Companion Planting Techniques
Companion planting means placing different plants together for their mutual benefits. Some benefits include:
- Deterring pests: Some plants can keep harmful insects away, protecting others.
- Enhancing growth: Plants like basil can make tomatoes taste better and grow more.
- Utilizing space: Mixing tall and short plants helps use sunlight better and avoid crowding.
Using companion planting makes your garden stronger and more productive. It follows the principles of good garden design and space use.
Utilizing Zones in Design
Permaculture zones help organize your garden by how often you visit it. Zones are set up like this:
| Zone | Description |
|---|---|
| Zone 0 | Your home or settlement. |
| Zone 1 | Highly cultivated area for daily harvesting, like herbs and salads. |
| Zone 2 | Less frequently visited, includes larger crops and small fruit trees. |
| Zone 3 | Pastures or orchards with minimal upkeep. |
| Zone 4 | Managed wildlife area, often for harvesting fuel. |
| Zone 5 | Unmanaged wilderness area, a natural habitat. |
Placing plants in these zones makes your garden easier to access and grow better. It also fits with your local climate, making your garden thrive. By following nature’s patterns, you can make a permaculture garden that suits your area perfectly.
Soil Preparation for Organic Gardening
Soil preparation is key to a successful organic garden. Knowing your soil’s condition is crucial for Soil Health. Start by doing Soil Testing to check nutrient levels and pH balance. This gives you a clear plan for your garden.
Testing Your Soil
Soil tests show what nutrients it has and what’s missing. This helps you choose the right Organic Amendments to improve it. You can get soil testing kits from local gardening centers or agricultural extensions. Here’s a quick guide to important soil tests and their benefits:
| Type of Test | Purpose | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Analysis | Measures levels of essential nutrients | Guides the selection of appropriate amendments |
| P.H. Testing | Determines soil acidity or alkalinity | Identifies if lime or sulfur is needed for balance |
| Texture Testing | Analyzes soil composition (sand, silt, clay) | Helps in understanding drainage and moisture retention |
Amendments for Healthier Soil
After testing your soil, you can pick the right Organic Amendments. These are crucial for keeping your soil healthy and your garden sustainable. Here are some effective methods:
- Add compost or organic mulch in spring and fall at a depth of 1-2 inches to enrich the soil.
- Incorporate green manures into the soil to contribute valuable nutrients as they decompose.
- Utilize sheet mulching to create new planting areas, minimizing soil disturbance.
- Resist the temptation to use chemical fertilizers, as they can harm soil microorganisms.
- Apply mulch to deter weeds, preventing them from germinating by blocking light.
These practices help make your garden more resilient and productive. By focusing on the soil, you create a thriving ecosystem. This ecosystem supports healthy plants and grows stronger every year.
Selecting the Best Plants for Your Climate
Knowing your local climate is key to picking the right plants. Native plants fit your area well, needing less care and boosting biodiversity. Gardening with the seasons helps grow crops that do well at certain times, giving you plenty to harvest. Think about these points when picking plants for your garden.
Native Plants for Easy Maintenance
Native plants are great for climate adaptation. They need less water and fight off pests and diseases, making care easy. Choose plants from within 100 miles of your home. This way, your garden fits right into the local ecosystem.
- Native plants have strong roots that keep soil moist.
- They help local wildlife, making your garden a healthy place.
- Examples of native plants include:
| Plant | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Black-eyed Susan | Attracts pollinators and tolerates drought. |
| Purple Coneflower | Supports local birds and resists disease. |
| Butterfly Weed | Serves as a magnet for butterflies and is adaptable to various soil types. |
Season-Appropriate Vegetables and Herbs
Using seasonal gardening ensures a bountiful harvest. Knowing which plants grow best in your area helps avoid failures. Since 2023, many places are now warmer, so you can grow more than before.
For the best harvest, pick these plants:
- Spring: Lettuce, peas, and radishes do well in cool weather.
- Summer: Tomatos, peppers, and basil love the heat.
- Fall: Kale, carrots, and garlic grow in cooler temps.
Plan your garden with plant selection in mind. Choose native plants and seasonal crops for a strong ecosystem and a better gardening experience.
Water Management in Permaculture Gardening
Effective water management is key to keeping your permaculture garden healthy. You can use strategies like rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation to save water. These methods help your garden stay strong, even in tough climates.
Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Rainwater harvesting is a smart way to collect and store water for your garden. You can use rain barrels, ponds, or swales to do this. These systems cut down on the need for city water and prevent pollution.
They’re especially good in places with lots of rain or where the soil gets too wet. They help meet permaculture’s environmental goals.
Drip Irrigation vs. Traditional Methods
Drip irrigation is a top choice for watering your garden. It delivers water right to the roots, unlike sprinklers that can lose water to evaporation and runoff. This makes it a great choice for saving water.
Here’s a quick look at how drip irrigation compares to traditional methods:
| Aspect | Drip Irrigation | Traditional Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High – minimizes waste | Low – potential for evaporation and runoff |
| Plant Health | Promotes deep root growth | May encourage shallow root systems |
| Labor Intensity | Requires initial setup time | Requires frequent manual watering |
| Long-Term Cost | Cost-effective over time | Higher due to water loss |
Using drip irrigation, especially in places like western Oregon or Scotland, can really help your garden use water better. Keeping the soil rich in organic matter helps it hold onto water. This means your plants do well when it’s dry and handle too much water when it rains.
Pest Management with Ecological Systems
Pest management is key to a healthy garden. Using ecological methods makes your garden sustainable and boosts its health. By supporting biodiversity and creating homes for good insects, you can keep pest numbers low without harsh chemicals.
Natural Predators and Their Role
Natural predators are vital for controlling pests. Attracting beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings helps. These insects eat pests, offering a green way to manage them. A diverse garden with many plants helps these predators thrive, making your garden healthier.
Organic Solutions for Common Pests
For organic gardeners, finding natural pest control is crucial. Methods like biological control, companion planting, and physical barriers work well. Cover crops improve soil and attract beneficial insects, helping prevent pest problems. These strategies help gardeners manage pests while keeping the garden balanced.

Maintaining Your Organic Garden Year-Round
Keeping an organic garden is a journey that never ends. It requires watching for seasonal changes and tasks. Regular care helps your plants stay healthy and strong.
Seasonal gardening tasks include planting native species in spring. You also need to apply organic mulch to keep moisture in. And, adjust your irrigation system to save water in hot months.
Using a drip irrigation system cuts down on water waste. It makes sure your plants get the right amount of water.
Seasonal Tasks to Keep Your Garden Thriving
Each season brings its own challenges and chances for growth. Late summer and early fall are great for planting fast-growing crops like spinach and carrots.
Introducing cover crops like clover or rye can also improve soil health. Keep an eye out for pests and diseases in summer. This helps you act fast.
Using companion planting can help control pests naturally. It makes your garden ecosystem vibrant.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Adaptation and learning are essential for organic gardeners. Watching how plants react to your garden’s conditions helps you improve. This way, you can make better choices about crop rotations and soil amendments.
Using organic matter like compost is beneficial. It acts as a slow-release fertilizer and boosts soil health and biodiversity. Continuous learning helps create a resilient permaculture garden that adapts to environmental changes.