A staggering 70% of the world’s biodiversity is found on just 2.5% of its land. This shows how urgent it is to use sustainable practices like permaculture. By using permaculture, people can make systems that help the environment and save natural resources.
This method of sustainable farming not only cuts down on carbon emissions. It also helps build strong, self-sufficient communities.
As we move towards greener ways of living, permaculture is becoming more important. It helps people make their living spaces better for the environment. This way, we can live in harmony with nature and help create a better future.
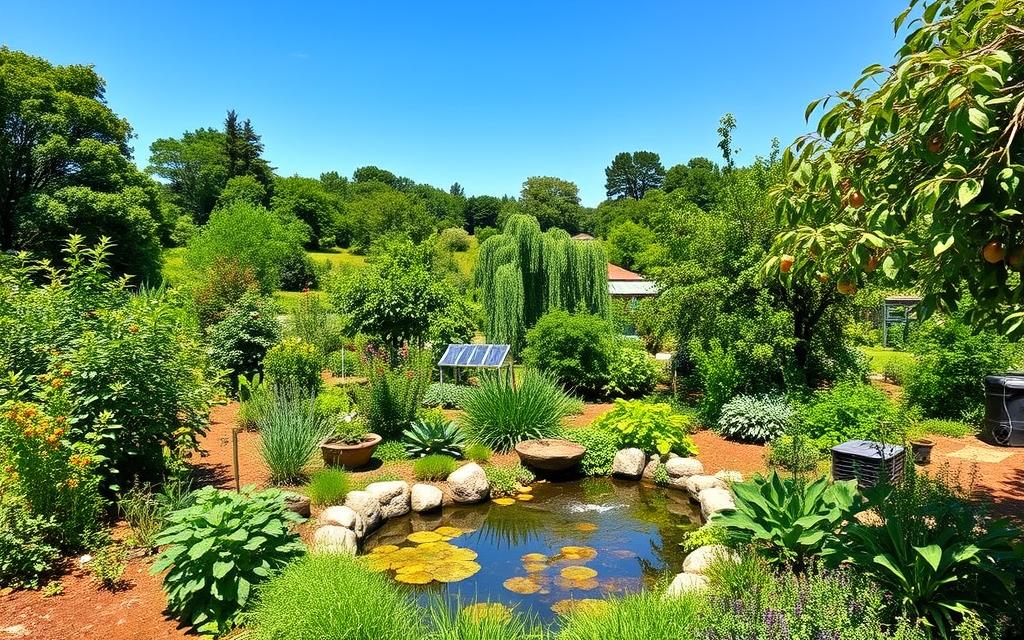

Understanding the Foundations of Permaculture Sustainable Living
Permaculture is a way of living that focuses on caring for the environment. It’s about creating systems that work well with nature. This means using farming methods that keep the soil healthy, support many different plants and animals, and help the ecosystem.
By following permaculture, we can help make the world a better place. It teaches us to think differently about how we live and interact with the environment. This helps us understand how everything is connected.
The Three Core Ethics of Permaculture
The three main ethics of permaculture are earth care, people care, and fair share. These ethics help guide how we design and use permaculture systems. They make sure these systems are good for the environment, fair for everyone, and work well economically.
Key Principles That Drive Sustainable Design
Important principles in permaculture include observing nature, catching and storing energy, and getting a good yield. These principles help us create systems that are strong, flexible, and productive.
The Historical Evolution of Permaculture
Permaculture has grown over time, shaped by many influences. It has been shaped by the wisdom of indigenous peoples, modern science, and movements for social justice. Knowing its history helps us see the depth and complexity of permaculture as a way of life.
| Core Ethics | Key Principles | Historical Evolution |
|---|---|---|
| Earth Care | Observe and interact with nature | Indigenous knowledge |
| People Care | Catch and store energy | Modern science |
| Fair Share | Obtain a yield | Social justice movements |
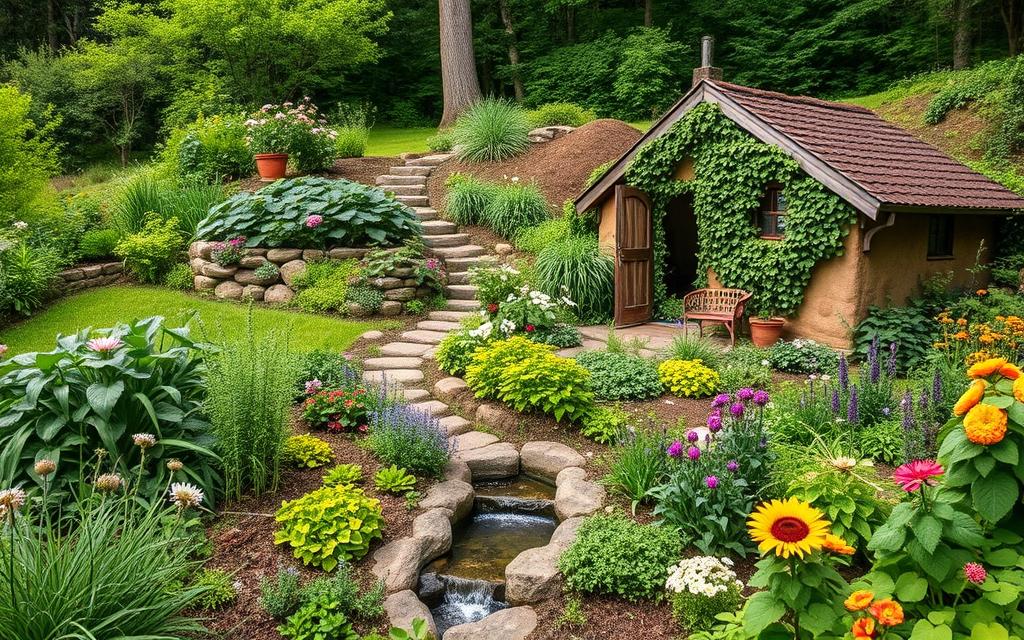

Creating Your Permaculture Zone System
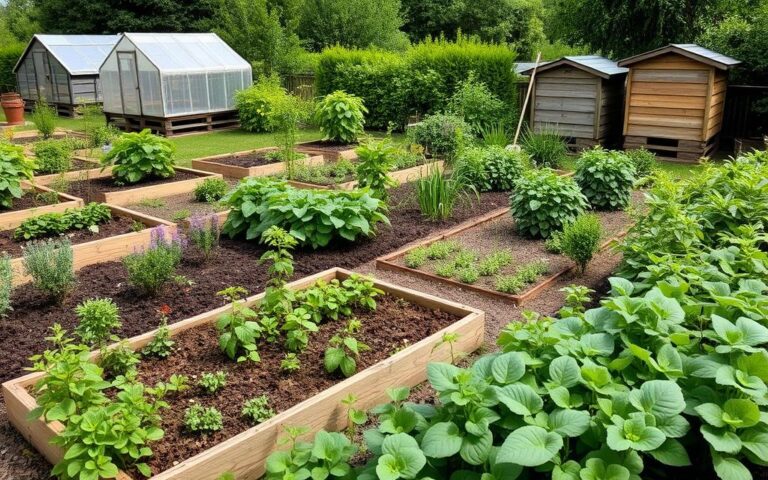
In organic gardening and plant-based permaculture, a well-designed zone system is key. It helps use space wisely, cuts down on energy, and boosts food output. By dividing your land into zones, you make your home more eco-friendly and self-sufficient.
A typical permaculture zone system has several zones, each with its own role. Zone 1 is right by the house, perfect for growing lots of food. Zone 2 is a bit further out, for less intense gardening and animal care, following plant-based permaculture rules.
When setting up your permaculture zone system, keep these points in mind:
- Check the climate and soil in each zone
- Plan zones for the best efficiency and output
- Use organic gardening and plant-based permaculture everywhere
By sticking to these guidelines, you can create a greener, more fruitful living space. This supports organic gardening and plant-based permaculture practices.
| Zone | Description |
|---|---|
| Zone 1 | Intensive organic gardening and food production |
| Zone 2 | Less intensive gardening and animal systems |
Essential Design Elements for Sustainable Spaces
Designing sustainable spaces means using eco-friendly practices. These practices help with sustainable agriculture. They include managing water well, using energy wisely, and reducing waste.
Water Management and Conservation
Water is very important and must be saved. To do this, we can use rainwater harvesting, greywater systems, and efficient irrigation. These methods help a lot.
- Rainwater harvesting
- Greywater systems
- Efficient irrigation systems
Energy Efficiency Solutions
Using energy wisely is key in sustainable design. Solutions like solar power and biogas help. They cut down on non-renewable energy use.
Waste Reduction Strategies
Keeping waste down is vital for sustainable agriculture. We can do this by composting and recycling. These actions help a lot.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Composting | Converting organic waste into nutrient-rich soil |
| Recycling | Converting waste materials into new products |
Building Fertile Soil Through Natural Methods
Regenerative design is key for a thriving permaculture system. It starts with fertile soil. Natural methods like compost, manure, and green manure improve soil. They also boost organic matter.
These methods are vital for holistic farming. They help soil biota and make ecosystems more resilient and productive.
Some important techniques for fertile soil include:
- Conservation tillage to reduce soil disturbance
- Cover cropping to add organic matter and nutrients
- Using compost and manure to enrich the soil
By using these natural methods, we can build a regenerative design. This supports holistic farming and a sustainable food system.
Healthy soil is the foundation of a healthy ecosystem. By using natural methods to build fertile soil, we can create a more sustainable and resilient food system.
Implementing Food Forest Systems
Food forests are key in permaculture, offering a variety of fruits, nuts, and more. They help keep ecosystems diverse and healthy. To make a food forest thrive, we need to pick plants that get along well.
When choosing plants, think about what they need to grow. They should like the same amount of sunlight and water. Also, make sure each plant has enough room to grow. This way, we can build a food forest that supports both permaculture and ecological living.
Selecting Compatible Plant Communities
- Choose species with similar growing conditions
- Consider the mature size of each plant
- Leave enough space for proper growth
Vertical Gardening Techniques
Vertical gardening boosts food production, even in small spaces. It’s great for city living where space is tight. With trellises, arbors, or wall planters, we can grow food forests in tiny areas.
Season Extension Methods
Methods like greenhouses or cold frames help grow food longer. They let us grow more crops and enjoy fresh food all year. This supports both ecological and permaculture living.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Greenhouses | Allow for year-round growing, regardless of external weather conditions |
| Cold Frames | Extend the growing season by protecting plants from frost and extreme temperatures |
Natural Resource Management in Permaculture
Managing natural resources well is key to a balanced ecosystem. This means using environmental stewardship and sustainable agriculture practices. These actions help reduce our environmental impact and make systems more regenerative.
Some important strategies for managing resources in permaculture include:
- Conserving water with efficient irrigation systems
- Boosting biodiversity with polycultures and agroforestry
- Using conservation agriculture to protect soil and improve its health
These strategies help us move towards a more sustainable future. Bill Mollison, a permaculture pioneer, once noted,
“The greatest change we need to make is from consumption to production, from being users to being creators.”
This change in mindset is crucial for adopting sustainable agriculture and environmental stewardship.
In summary, managing natural resources is essential in permaculture. By focusing on environmental stewardship and sustainable agriculture, we can build a more regenerative and balanced ecosystem.
Creating Sustainable Animal Systems
Permaculture teaches us about the importance of animals in our ecosystem. By using holistic farming, we can make our environment more balanced and sustainable. This means picking animals that do well in our local climate and working them with plants to help each other out.
Using eco-friendly methods, like local feed and less waste, helps animals not harm the environment. Important steps for sustainable animal systems include:
- Choosing the right animals for our climate and ecosystem
- Rotating animals to keep the soil healthy and diverse
- Feeding animals naturally and organically to avoid industrial farming
By following these holistic farming methods, we can build a stronger and greener food system. Looking at successful permaculture farms and animal systems can inspire us to be more eco-friendly.
The secret to sustainable animal systems is a holistic and integrated farming approach. By working with nature, we can make a better home for all living things.
| Livestock | Climate | Feed Source |
|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Temperate | Grass-fed |
| Chickens | Tropical | Organic grain |
| Pigs | Temperate | Locally sourced |
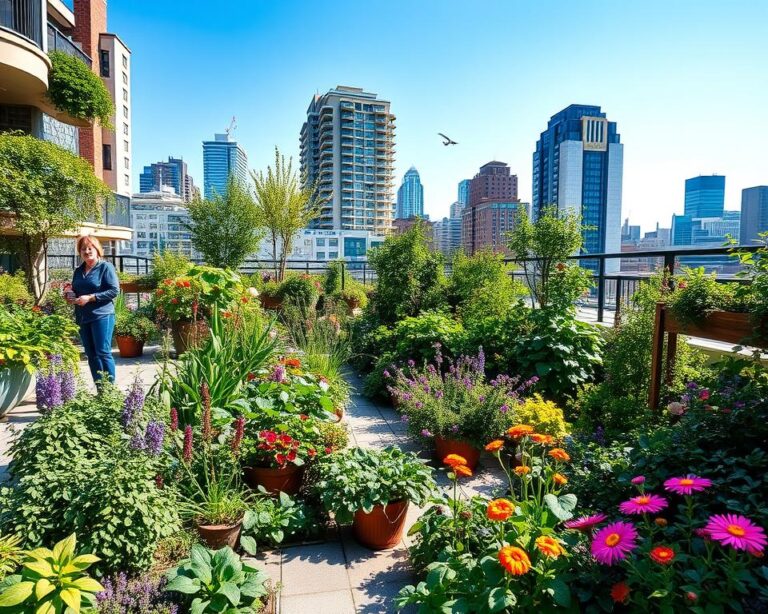
Urban Permaculture Solutions
As cities grow, it’s key to use permaculture sustainable living in city planning. This means using regenerative design to make cities sustainable and self-sufficient. Urban permaculture applies these ideas to cities and towns.
Some examples of urban permaculture solutions include:
- Community gardens, where people can grow their own food and connect with nature
- Green roofs, which cut down on pollution and save energy
- Urban farms, which give fresh food to local people and ensure food security
By using permaculture sustainable living in city planning, cities can become greener and stronger. This is done through regenerative design and getting the community involved. As more people want sustainable living, urban permaculture is key in city planning.
We can make cities better by working together. We can focus on permaculture sustainable living and regenerative design. This is done through community efforts, education, and new design ideas.
| Urban Permaculture Solution | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Community Gardens | More food, community ties, and better mental health |
| Green Roofs | Less pollution, more energy savings, and cleaner air |
| Urban Farms | Fresh food, jobs, and community growth |
Economic Aspects of Permaculture Living
Permaculture living is more than just growing food and living green. It’s about building a strong economy too. People can make a living and help their local communities by using permaculture. This is done through organic farming, eco-tourism, and community-supported agriculture.
Community exchange systems are a big part of permaculture. They let people trade goods and services without money. For instance, a group might share tools instead of buying new ones. This saves money, reduces waste, and builds community.
Building Sustainable Livelihoods
Creating jobs that are good for the planet is key in permaculture. This can be done by starting businesses like organic farming, eco-tourism, and sustainable forestry. These jobs not only make money but also help the environment. Here are some examples:
- Organic farming: growing food naturally
- Eco-tourism: offering tours and stays that support green living
- Sustainable forestry: cutting trees in a way that helps forests grow back
Marketing Permaculture Products
It’s important to sell permaculture products to spread the word about living green. This can be done at farmers’ markets, online, and through community programs. Selling these products helps support local businesses and promotes sustainable living. For example, a weekly farmers’ market can help local farmers sell their organic produce.
| Product | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Organic vegetables | Fresh, locally grown vegetables | $3.00/lb |
| Eco-friendly soap | Handmade soap made from natural ingredients | $5.00/bar |
| Sustainable wood products | Wood products made from sustainably harvested trees | $10.00/each |
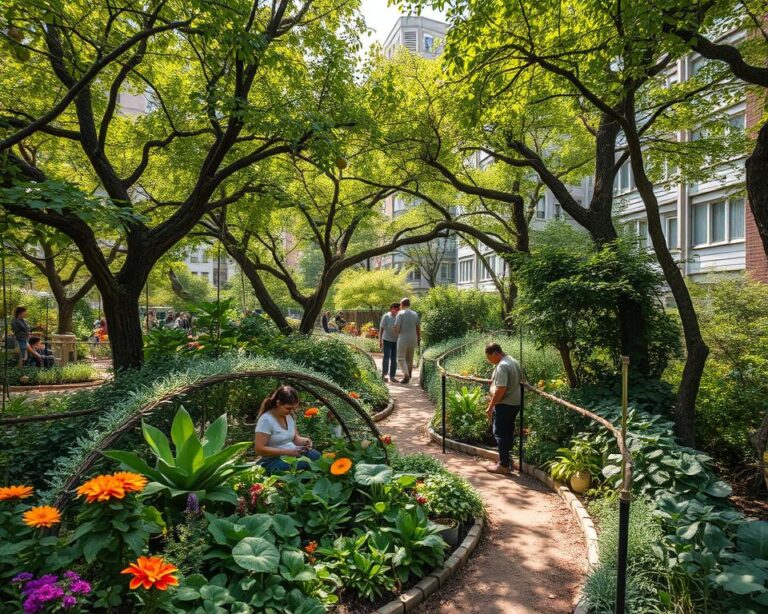
Social Dimensions of Permaculture Communities
Permaculture communities focus on holistic farming and environmental stewardship. They aim to build inclusive and fair societies. These groups work on social justice and caring for the environment through different projects.
Some key aspects of permaculture communities include:
- Building community gardens to promote social cohesion and cooperation
- Implementing cooperative living arrangements to foster a sense of community
- Establishing participatory decision-making processes to ensure everyone’s voice is heard
Permaculture communities help build stronger, sustainable places. They focus on bringing people together. This is key for a better future for everyone.
As permaculture communities grow, they’ll play a bigger role in caring for our planet. By supporting each other, they can make our world more sustainable and fair for all.
Conclusion: Embracing the Permaculture Journey
As we wrap up our look at permaculture sustainable living, it’s clear it’s a game-changer. It offers a way to live in harmony with nature and build a better future. By following permaculture’s principles, we can live in a way that’s good for the planet, fair to all, and financially sound.
The journey of permaculture is never-ending, full of chances to learn and grow. We must stay curious and work together to find new ways to solve big problems. By using permaculture design, we can create strong, self-sufficient communities that respect the Earth’s natural flow.
Choosing to follow the permaculture path is a bold move towards a better tomorrow. It’s a chance to make a difference and help create a brighter, greener world. Let’s keep exploring and using permaculture’s power to build a world that’s full of life and possibility.
FAQ
What is permaculture and how does it relate to sustainable living?
Permaculture is a way to design our living spaces to be better for the environment. It makes our homes and gardens more self-sufficient and in tune with nature. By using permaculture, we can lower our carbon footprint and help the planet.
What are the three core ethics of permaculture?
Permaculture’s core ethics are earth care, people care, and fair share. These guide us to make our systems sustainable, fair, and beneficial for everyone.
How can I create a permaculture zone system on my property?
Divide your property into zones based on how close they are to your home. Zone 1 is closest and best for growing food. Zone 2 is further out for less intensive gardening. This way, you use space wisely and grow more food.
What are some essential design elements for sustainable spaces in permaculture?
Key elements include managing water, using solar power, and reducing waste. Rainwater harvesting, greywater systems, and composting are all important. They help save energy and resources.
How can I build fertile soil through natural methods in a permaculture system?
To make fertile soil, use compost, manure, and green manure. Also, try conservation tillage and cover cropping. These methods improve soil health and make it more productive.
What is a food forest system in permaculture, and how can I implement one?
Food forests are diverse gardens that grow many edible plants. To start one, pick the right plants and use vertical gardening. Season extension methods help grow food longer.
How can I incorporate sustainable animal systems into my permaculture design?
Adding animals to your permaculture is key. Choose the right animals and integrate them with plants. Use sustainable feed to reduce environmental impact.
What are some urban permaculture solutions that I can apply in my community?
Urban permaculture means using green spaces in cities. Create gardens, green roofs, and urban farms. It also means using sustainable transport and energy. These actions help clean cities and feed people.
How can I build sustainable livelihoods and promote local economies through permaculture?
Permaculture helps create jobs and support local economies. Start sustainable businesses like organic farming. Use community exchange systems and market permaculture products. This way, you help fight poverty and support fairness.