Did you know permaculture can increase soil carbon by 27% compared to traditional farming? This shows how vital soil health is in permaculture and organic gardening. Healthy soil is key to a thriving ecosystem, adding organic matter and boosting biodiversity.
It also supports plant growth. Sustainable gardening focuses on reducing soil disturbance and improving nutrient cycling. This creates a home for beneficial microorganisms.
By choosing eco-friendly gardening, you’re building a connected environment. Practices like crop diversity and contour planting improve soil structure and nutrient levels. These methods also boost soil productivity. Let’s explore why soil health is crucial in permaculture systems, ensuring your plants grow strong and healthy.
Understanding Organic Gardening and Permaculture
Organic gardening and permaculture are two ways to garden sustainably. They both aim to live in harmony with nature and care for the environment. You’ll learn about their main ideas and what makes them unique.
What Is Organic Gardening?
Organic gardening grows plants without using synthetic fertilizers or pesticides. It uses natural methods to keep soil healthy and support many different plants. This approach started in the 1940s and has grown into a big industry.
It focuses on soil health, saving water, and controlling pests naturally. Organic gardening uses techniques like rotating crops and using natural materials. It highlights the connections between gardening and the environment.
What Is Permaculture?
Permaculture started in the 1970s and builds on organic gardening. It aims to create farms that work like natural ecosystems. This movement promotes sustainability and local food production.
Permaculture grows many different crops and aims for self-sufficiency. It uses gardening methods that protect the environment. This helps both people and nature.
Key Principles of Permaculture
The core of permaculture is based on several key principles. These include:
- Embrace Diversity: Growing many types of crops helps prevent pests and keeps ecosystems stable.
- Build Healthy Soils: Healthy soil is key, and natural composting is used instead of chemicals.
- Cycle Nutrients: Recycling nutrients in ecosystems keeps soil fertile and reduces waste.
- Integrate Practices: Mixing different farming methods can use resources better.
- Care for the Earth: Working in harmony with nature ensures a sustainable future.
The Role of Soil Health in Organic Gardening
Soil health is key to a successful organic garden. It supports processes like nutrient cycling and a diverse community of microorganisms. Knowing these elements helps you grow a vibrant organic garden.
Nutrient Cycling
Nutrient cycling is vital in organic gardening. Compost and plant residues break down, turning into nutrients for plants. This cycle helps plants grow strong and keeps the soil fertile.
Soil Diversity
Soil diversity makes the ecosystem richer. It encourages many plant species and beneficial organisms. Different plants and their residues improve soil health and make it more resilient against pests and diseases.
Microorganisms and Soil Health
Microorganisms are crucial for soil health. They break down organic matter and improve soil structure. A healthy mix of microorganisms makes nutrients available and helps retain water, creating a great environment for plants.
Practices that support these elements greatly improve your organic gardening. A healthy soil ecosystem not only boosts plant health but also supports sustainable farming, benefiting the environment.
Benefits of Healthy Soil in Permaculture
Healthy soil is key for thriving permaculture systems. It helps plants grow better, increases crop yields, and fights climate change. By taking care of the soil, you build a system that supports life and is good for the planet.
Enhanced Plant Growth
Healthy soil is vital for plant growth. It’s full of good microbes that make nutrients available to plants. This lets plants grow strong and healthy.
Having different plants cover the soil. This creates a network that helps all plants grow better. Plants also keep the soil cool, which helps everything grow.
Improved Crop Yields
Soil health means better crops. Healthy soil makes the land more fertile and cuts down on the need for harmful chemicals. This way, you get more food that’s also better for you.
This is especially important as we face climate change. It helps ensure we have enough food and it’s nutritious.
Resilience to Climate Change
Healthy soil helps fight climate change. It absorbs rain, preventing floods and soil loss. It also helps capture carbon dioxide, which fights global warming.
By improving soil health, you’re not just growing food. You’re also helping the planet. It’s a win-win for everyone.
Building Soil Health: Key Practices
Improving soil health is key for organic farming and permaculture. Practices like composting, crop rotation, and mulching are essential. They help with fertility, pest control, and caring for the environment, making your garden or farm better.
Composting Techniques
Composting turns organic waste into nutrient-rich soil. You can make compost from kitchen scraps and yard waste. It improves soil structure and keeps it moist. Make sure to mix carbon-rich and nitrogen-rich materials for the best compost.
Crop Rotation Strategies
Crop rotation boosts soil health. It means changing what you grow in a spot over time. This stops nutrients from getting used up and keeps pests and diseases away. Legumes, for example, add nitrogen back into the soil, helping your crops grow well every year.
Mulching Methods
Mulching helps keep soil moist and stops weeds. Use organic materials like straw or wood chips. A 2- to 4-inch layer in spring works best. As it breaks down, it adds nutrients and protects the soil from erosion and extreme temperatures.
| Practice | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Composting | Enhances soil fertility and structure, increases moisture retention |
| Crop Rotation | Prevents nutrient depletion, reduces pests, and disease |
| Mulching | Retains moisture, suppresses weeds, and enriches soil |
Using these practices together creates a strong, healthy soil ecosystem. It’s vital for the success of your organic garden and permaculture projects.
Soil Testing: Know Your Soil
Knowing your soil’s health is key for a successful organic garden. Soil testing shows you nutrient levels and pH balance. This helps you choose the right soil amendments.
Types of Soil Tests
There are many ways to test your soil. Two main types are:
- pH Testing: Shows if your soil is too acidic or too alkaline, which affects nutrient use.
- Nutrient Analysis: Checks for nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which plants need to grow.
Interpreting Soil Test Results
Understanding your soil test results is crucial. Here’s what to remember:
- Nitrogen helps plants grow green leaves.
- Phosphorus is important for flowers and fruits.
- Potassium helps with photosynthesis and keeps plants healthy.
The results will tell you what your soil lacks. This helps you choose the right amendments.
Adjusting Soil Amendments
After you know what your soil needs, you can improve it. Here are some good options:
- Compost: Makes soil better for plants and holds water.
- Bark and Leaf Mold: Keeps soil moist and lets air in.
- Manure: Adds nutrients and makes soil better.
Choosing organic amendments based on your test results can really help your garden grow.
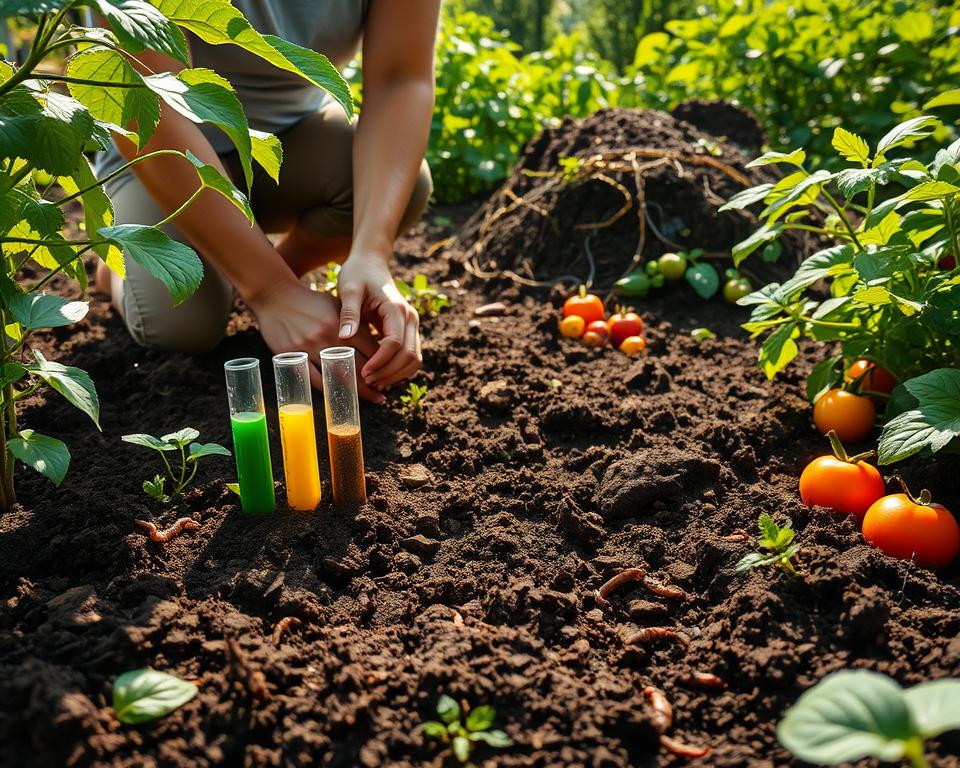

| Soil Component | Function | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Supports leaf growth | Compost, Manure |
| Phosphorus | Encourages flowering | Bone Meal, Rock Phosphate |
| Potassium | Aids photosynthesis | Wood Ash, K-Mag |
Testing your soil every three years is good for home gardeners. Farmers should do it every year. This keeps your soil balanced and good for your garden. Using the right amendments based on your tests helps plants grow better and improves soil quality.
Cover Crops and Their Importance
Cover crops are key in sustainable gardening. They help keep soil healthy in many places. They keep the soil in good shape and stop it from washing away. By using cover crops, your garden will get better and so will the environment.
Benefits of Using Cover Crops
Using cover crops has many good points for gardeners and farmers:
- Soil Erosion Prevention: Their roots hold the soil in place, stopping it from washing away.
- Nutrient Retention: They grab nutrients from the soil, making it richer and cutting down on chemical use.
- Improvement of Soil Structure: They add organic matter, helping the soil hold water better and letting it soak up more.
- Weed Suppression: They grow faster than weeds, keeping them from taking over your garden.
- Pest and Disease Management: Some types can fight off diseases in the soil, making your garden healthier.
Popular Cover Crop Choices
Here are some top cover crops for your garden:
- Clover: It fixes nitrogen and is good for bees and butterflies.
- Vetch: It adds to the soil’s organic matter, making it healthier.
- Rye: It’s tough and keeps weeds down with little work needed.
Managing Cover Crops Effectively
To get the most from cover crops, manage them well. Here’s how:
- Timing: Plant them between crops or after you harvest for the best soil benefits.
- Seed Density: Plant them thick to cover the ground and fight weeds.
- Fertilization: Give them the right food to grow more, adding more organic matter to your soil.
- Seedbed Preparation: Start with a clean bed to help them grow better.
The Impact of Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is a big problem for gardeners and farmers. It slowly takes away the top layer of soil, called topsoil. This layer is full of nutrients that plants need to grow well.
Causes of Soil Erosion
Soil erosion happens for many reasons:
- Water runoff
- Wind
- Poor agricultural practices
Heavy rains and strong winds can wash or blow away soil without protection. Animals eating too much grass and removing plants also make erosion worse.
Effects on Soil Quality
Soil erosion has big effects:
- Nutrient availability
- Water retention
- Risk of flooding
Without topsoil, plants don’t get the nutrients they need. This can make crops smaller and land less valuable. Plants’ roots can also get pulled out of the ground more easily.
Preventive Measures for Erosion
There are ways to stop soil erosion:
- Implementing terraced farming on hillsides to slow runoff
- Restoring natural vegetation by replanting trees to hold soil in place
- Planting ground covers and using mulch to shield the soil from rain impact
- Creating windbreaks with shrubs or trees to diminish wind velocity
Using sustainable gardening and permaculture helps your garden and the environment. With the right care, you can make your soil better for the future.
Water Management and Soil Health
Effective water management is key to keeping soil healthy in organic gardens. Soils with organic matter hold water better. This helps plants grow strong and makes gardens more resilient.
Importance of Water Retention
Soil health depends on water retention. Soils with organic matter can hold more water. This means less need for watering, especially during dry times.
Techniques for Managing Water
There are ways to manage water better in your garden. Here are some:
- Mulching: Organic material on top of the soil keeps it moist and stops weeds.
- Swales: These features catch and direct water, letting it soak into the soil.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting rainwater cuts down on the need for city water and is good for irrigation.
Irrigation Best Practices
Using water wisely is important. Here’s how:
- Drip Irrigation: Water goes straight to the roots, saving water and reducing waste.
- Timing Adjustments: Water in the morning or evening to cut down on evaporation.
- Regular Monitoring: Check soil moisture to water plants when they need it, avoiding too much.
Challenges in Maintaining Soil Health
Keeping soil healthy is key for gardening that lasts. Pests, compaction, and seasonal changes can harm your soil. Knowing these problems helps you find ways to keep your soil in top shape.
Pests and Diseases
Pests can upset the balance in your soil’s tiny ecosystems. This can mess up how nutrients are cycled. Instead of using lots of chemicals, try using methods that protect your soil and the environment.
Compaction Issues
Soil compaction is a big problem for many gardeners. It stops roots from growing and makes it hard for water to get in. To fix this, aerate your soil and avoid using heavy machines. Adding organic matter helps too.
Seasonal Changes and Their Effects
Seasons change how much water your soil holds and its temperature. This affects your soil’s health. By knowing these changes, you can adjust your gardening to keep your soil healthy all year.
Resources for Further Learning
To learn more about soil health and organic gardening, many resources are available. Books on organic gardening offer insights and practical tips. They help improve soil fertility and teach permaculture practices.
Books like “The Organic Gardener’s Handbook of Natural Pest and Disease Control” and “Teaming with Microbes” are great. They cover the basics of healthy soil.
Recommended Books on Organic Gardening
Online courses and workshops are also great for learning. Sites like Coursera and Udemy have courses on organic gardening and permaculture. These resources let you learn at your own pace.
You can explore topics like composting, crop rotation, and planting techniques. This way, you can learn what works best for your garden.
Online Courses and Workshops
Joining local gardening groups and forums is another good idea. Many communities have gardening clubs and workshops. Here, you can meet experienced gardeners, share ideas, and learn by doing.
These gatherings are supportive and can help you grow a successful organic garden. They offer a place to learn and grow together.